Sales Pipeline vs Sales Funnel: Understanding the Key Differences and Choosing the Right One for Your Business

Key Points
- Sales pipeline and sales funnel are distinct approaches to managing the sales process, with one focusing on stages and actions, and the other on the buyer’s journey.
- Understanding the key differences between sales pipeline and sales funnel transforms sales processes, marketing efforts, and business success.
- Considerations such as business nature, target audience, and sales goals should guide business decisions in selecting the appropriate approach, be it sales pipeline or sales funnel.
Introduction
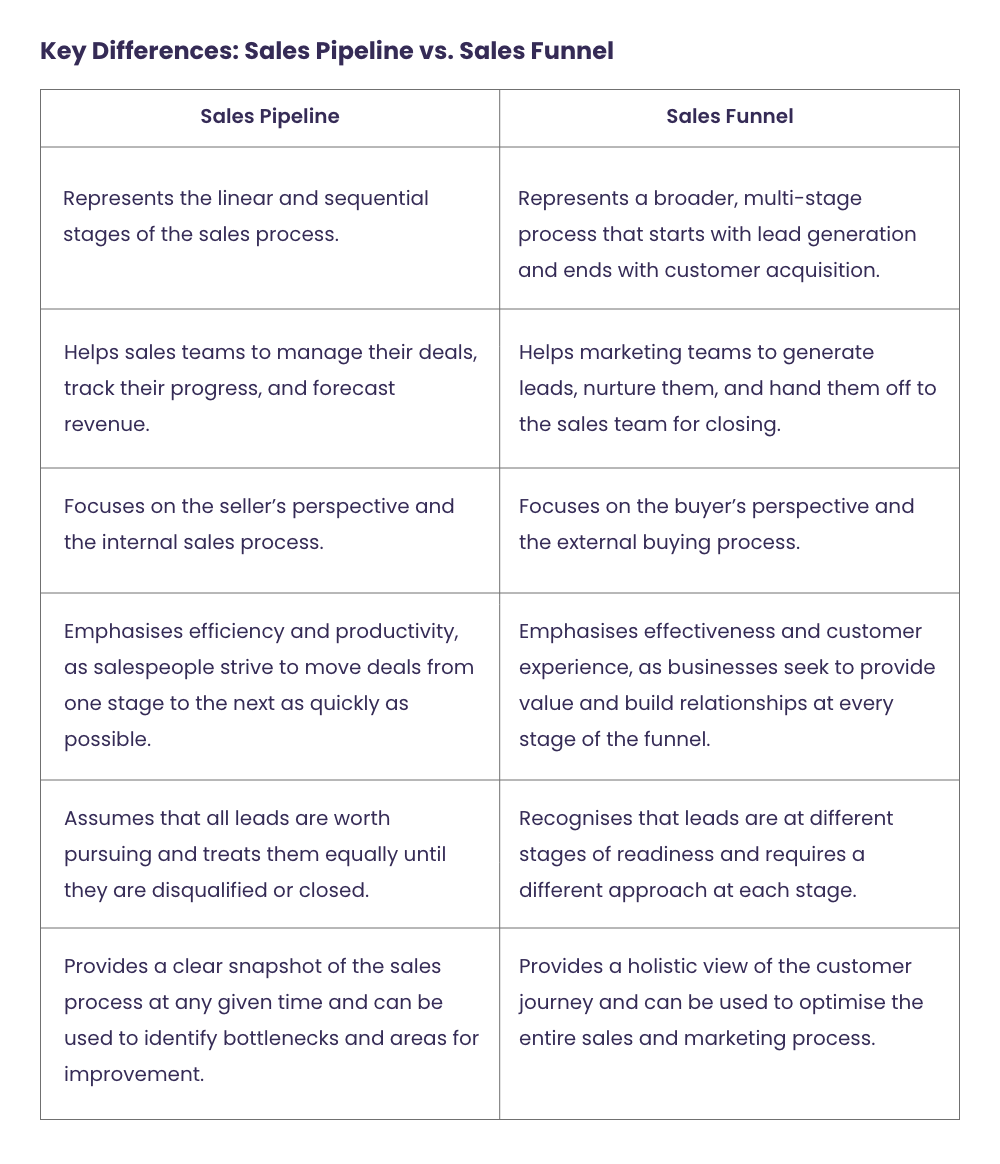
In the world of sales, having a clear understanding of the different stages a potential customer goes through before making a purchase is crucial to success. Two common terms often used interchangeably but have distinct differences are sales pipeline and sales funnel. While both terms describe the process of converting prospects into customers, they differ in their approach and the level of detail they provide. Understanding the key differences between these concepts is essential for any business looking to optimise its sales process and improve its overall revenue. In this blog, we’ll explore the differences between sales pipeline and sales funnel and help you determine which one is the right fit for your business.
Sales Pipeline: A Closer Look
A sales pipeline is a systematic approach businesses use to manage and track the progress of their sales process, from lead generation to closing the sale. It represents the stages of the sales process and the probability of closing a sale at each stage. The sales pipeline operations typically consists of stages such as prospecting, qualifying, proposal, negotiation, and closing. It helps sales teams to prioritise their efforts, identify and address bottlenecks, and forecast revenue. By tracking the progress of each lead through the pipeline, businesses can better manage their resources and increase the effectiveness of their sales efforts.
Stages and Key Components of a Sales Pipeline:
A typical sales pipeline consists of several stages that align with the different phases of the buyer’s journey. These stages may vary depending on the nature of the business but generally include the following:
- Prospecting: The first stage of the sales pipeline involves identifying potential customers or leads that fit the ideal customer profile. This involves researching the market, gathering information on prospects, and reaching out to them to initiate contact.
- Key components:
- Identifying the target market or customer segment
- Researching leads and creating a database
- Initiating contact with prospects through various channels such as cold calling, email campaigns, or social media outreach.
- Key components:
- Qualification: In this stage, sales representatives qualify the leads based on certain criteria to determine whether they have the potential to become customers. This involves evaluating whether the lead has a need for the product or service, whether they have the authority to make a purchase decision, and whether they have the budget to purchase.
- Key components:
- Evaluating whether the lead fits the ideal customer profile
- Determining the level of interest and commitment
- Assessing whether the lead has the authority, need, and budget to make a purchase decision.
- Key components:
- Needs Analysis: This stage involves a deeper exploration of the customer’s needs and requirements. The sales representative needs to understand the customer’s pain points, challenges, and goals to provide relevant solutions that address their needs.
- Key components:
- Understanding the customer’s requirements and pain points
- Identifying the customer’s goals and objectives
- Demonstrating how the product or service can address the customer’s needs.
- Key components:
- Proposal: In this stage, the sales representative presents a customised proposal that outlines the recommended solution for the customer’s needs. This includes pricing, terms and conditions, and other relevant details.
- Key components:
- Creating a customised proposal that addresses the customer’s requirements
- Presenting the proposal to the customer
- Addressing any questions or concerns the customer may have.
- Key components:
- Negotiation: In this stage, the sales representative negotiates the terms of the sale with the customer. This includes discussing pricing, payment terms, and any other relevant details.
- Key components:
- Negotiating pricing and other terms with the customer
- Finding a mutually acceptable solution
- Addressing any objections or concerns the customer may have.
- Key components:
- Closing: The final stage of the sales pipeline involves securing the sale. This involves getting the customer’s agreement to move forward with the purchase and finalising the transaction.
- Key components:
-
-
- Obtaining the customer’s agreement to move forward with the purchase
- Finalising the transaction and delivering the product or service
- Ensuring customer satisfaction and addressing any post-sale issues.
-
Benefits and Limitations of Using a Sales Pipeline:
Using a sales pipeline offers several benefits for businesses, including:
- Improved sales visibility: A sales pipeline provides a clear overview of the sales opportunities at different stages, allowing sales teams to prioritise their efforts and allocate resources effectively.
- Better sales forecasting: A sales pipeline helps businesses forecast revenue based on the opportunities in the pipeline and the conversion rates at each stage, providing valuable insights for budgeting and planning.
- Enhanced sales accountability: A sales pipeline establishes a standardised sales process with defined stages, milestones, and actions, which helps sales reps stay organised, focused, and accountable for their sales activities.
- Streamlined sales management: A sales pipeline enables sales managers to track the progress of each opportunity, identify bottlenecks, and provide timely coaching and support to their sales team.
However, there are also limitations to using a sales pipeline, such as:
- Over-reliance on the process: A sales pipeline can create a rigid and overly structured sales process that may not be flexible enough to adapt to changes in the market or customer needs.
- Lack of individuality: A sales pipeline can overlook the unique needs of individual customers, leading to a one-size-fits-all approach that may not be effective.
- Incomplete information: A sales pipeline relies on accurate and up-to-date information about each deal, and incomplete or inaccurate information can lead to inaccurate forecasting and resource allocation.
- Complexity: A sales pipeline can be complex and difficult to implement, requiring significant time and resources to set up and maintain.
Examples of Businesses That Can Benefit from a Sales Pipeline:
Businesses that can benefit from a sales pipeline include, but are not limited to:
- Real estate agencies: Sales pipelines can help agents keep track of potential buyers, their budgets, and preferences and ensure a streamlined sales process.
- Consulting firms: Sales pipelines can help consulting firms keep track of prospective clients, their requirements, and follow-up actions and ensure a seamless sales process.
- Software companies: Sales pipelines can help software companies track prospects, preferences, and buying behaviour and ensure a successful sales process.
- Financial services companies: Sales pipelines can help financial services companies keep track of potential clients, their requirements, and preferred financial products and ensure a smooth sales process.
- Marketing agencies: Sales pipelines can help marketing agencies keep track of prospects, their needs, and buying behaviour, and ensure an effective sales process.
Sales Funnel: Unveiling The Insights
A sales funnel is a visual representation of the customer journey from the moment they become aware of a product or service to the point of making a purchase.
It’s called a “funnel” because it represents the gradual narrowing of potential customers as they move through different stages of the sales process, with the ultimate goal of converting them into paying customers. The typical stages of a sales funnel include awareness, interest, consideration, and decision, and each stage involves specific marketing tactics and strategies aimed at guiding potential customers towards the final purchase.
The purpose of a sales funnel is to provide a clear understanding of the customer journey and help businesses identify areas where they can improve the sales process to increase conversions and revenue.
Phases and Crucial Elements of a Sales Funnel:
A typical sales funnel consists of several phases or stages that align with the different steps of the buyer’s journey. These phases may vary depending on the nature of the business but generally include:
- Awareness: This is the initial stage where potential customers become aware of a business or its products/services. Key elements of this stage include marketing strategies such as content marketing, social media marketing, and search engine optimisation (SEO) to generate awareness and attract potential customers.
- Interest: Once potential customers are aware of a business, they may show interest in learning more about the products/services offered. Key elements of this stage include lead generation, landing pages, and email marketing to capture leads and nurture their interest.
- Consideration: In this stage, potential customers actively evaluate the products/services offered and compare them with competitors. Key elements of this stage include product demonstrations, customer testimonials, and case studies to build trust and influence the decision-making process.
- Decision: Once potential customers are convinced of the value of the products/services, they move to the decision stage where they are ready to make a purchase decision. Key elements of this stage include sales presentations, pricing discussions, and overcoming objections to encourage the purchase.
- Action: After the decision is made, potential customers take action by making a purchase or signing up for a service. Key elements of this stage include seamless checkout processes, order confirmation, and post-purchase follow-up to ensure customer satisfaction.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using a Sales Funnel:
Using a sales funnel offers several advantages for businesses, including:
- Clear customer journey: A sales funnel provides a clear path for potential customers to move through each stage of the buying process, helping businesses understand customer behaviour and tailor their marketing and sales efforts accordingly.
- Better conversion rates: A well-structured sales funnel can help businesses optimise their marketing and sales strategies at each stage, resulting in improved conversion rates and higher revenue.
- Improved lead nurturing: A sales funnel allows businesses to nurture leads at each stage, providing the right information and offers at the right time, which can result in increased customer engagement and loyalty.
- Streamlined sales process: A sales funnel provides a structured framework for businesses to follow, helping them streamline their sales process, identify bottlenecks, and optimise their sales efforts.
However, there are also limitations to using a sales funnel, including:
- Simplistic view: A sales funnel provides a simplified view of the customer journey, which may not always capture the complexity of customer behaviour and decision-making process.
- One-size-fits-all approach: A sales funnel may not be suitable for businesses with diverse customer segments or complex sales processes that require a more personalised approach.
- Potential for loss of opportunities: A sales funnel may lead businesses to overlook potential opportunities that fall outside the defined stages of the funnel.
Instances Where a Sales Funnel is Preferable for Business:
Businesses that can benefit from a sales funnel include, but are not limited to:
- E-commerce businesses: Sales funnels can help e-commerce businesses increase their conversion rates by guiding visitors from initial awareness to making a purchase.
- Coaching and training businesses: Sales funnels can help coaching and training businesses convert leads into customers by providing valuable information and building trust over time.
- Health and wellness businesses: Sales funnels can help health and wellness businesses promote their products and services, educate their audience, and convert leads into loyal customers.
- Digital product businesses: Sales funnels can help digital product businesses convert leads into paying customers by offering free trials, demos, and special offers.
- Non-profit organisations: Sales funnels can help non-profit organisations generate donations and raise awareness by building relationships with donors and supporters over time.
Considerations For Choosing The Right Strategy For Your Business
The choice between a sales pipeline and a sales funnel depends on various factors, including the nature of business, the complexity of the sales process, and sales goals. Here are some factors to consider:
Sales process complexity: A sales funnel is typically used for a more complex sales process where a potential customer requires multiple touchpoints and interactions with the business before making a purchase. A sales pipeline may be more suitable if your sales process is more straightforward.
Buyer’s journey: A sales funnel focuses more on the customer’s journey and can help you understand the various stages of customer awareness, consideration, and decision-making. A sales funnel may be the right choice if you need to develop a more detailed customer journey map.
Sales team structure: A sales pipeline is often used to track the progress of individual deals through different stages of the sales process. If you have a larger sales team, a pipeline may help you better manage and track individual sales reps’ progress.
Marketing and sales alignment: A sales funnel is more aligned with marketing, whereas a sales pipeline is more aligned with sales. A sales funnel may be more helpful if you need to better align your marketing and sales teams.
Business goals: Ultimately, choosing between a sales funnel and a sales pipeline depends on your business goals. A sales funnel may be the right choice if you need to increase your customer base. A sales pipeline may be more appropriate if you need to improve your sales team’s productivity.
Conclusion
Understanding the key differences between sales pipeline and sales funnel is crucial for designing an effective sales process that aligns with business goals. While the sales pipeline follows a sequential and deal-specific approach, the sales funnel takes a holistic and lead-centric approach, encompassing the entire customer journey. It’s important to choose the right sales strategy for business based on factors such as the complexity of the sales cycle, the type of products or services the business offers, and the preferences of their target audience.
Regularly evaluating and optimising sales processes is essential for sustained business success. By continuously monitoring and measuring the effectiveness of sales strategies, businesses can drive revenue growth, build strong customer relationships, and achieve their objectives. There is no one-size-fits-all approach, and it’s crucial to align sales efforts with unique business needs and goals. By staying agile and responsive to market changes, businesses can adapt and optimise their sales processes to stay ahead in today’s competitive business landscape.